
A master training log provides a single source of truth for all your team’s training records and forms the backbone of an audit-ready compliance file. This master training log should capture employee names, course titles, completion dates and certificate validity to satisfy any auditor’s requirements. Building a robust master training log demonstrates control over your training program and offers traceable proof of staff competency.
This blog provides life-science quality professionals with an in-depth guide to the training documents auditors expect. You will learn which records to collect, how to organise them for rapid retrieval and how GxP Training’s Regulatory Compliance Inspections and External Audits course equips your team with accredited, traceable certificates and practical insights.
Regulatory bodies such as the World Health Organization and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration regard documented training as proof of control over quality systems. ICH Q10 requires companies to maintain a robust quality management system that includes comprehensive training records. Pharmaceutical and device manufacturers must demonstrate that personnel have received instruction on SOPs, safety protocols and change-control processes before performing assigned tasks.
Inspectors typically evaluate whether your records answer three fundamental questions. Who completed the training, what material they covered and when it occurred. Missing completion dates, unsigned attendance sheets or unclear course titles can raise doubts about staff competency. Electronic training logs must comply with FDA 21 CFR Part 11, capturing user ID, date-time stamps and an immutable audit trail. European inspectors will also review compliance with local requirements under the EU GMP Annex 11 for computerized systems. Clear alignment between your training curriculum, regulatory guidelines and recorded evidence builds confidence in your control over quality systems.
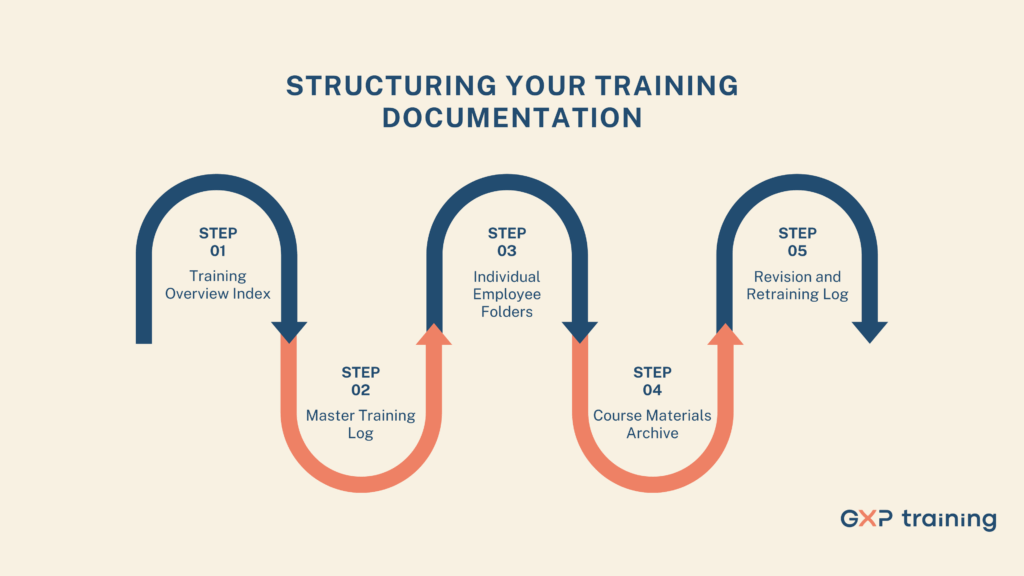
Well-organised training documentation accelerates audits and reduces the risk of findings. A logical folder framework or binder layout helps auditors locate required records in seconds.
This framework creates transparency, traceability and user-friendly access. Auditors will appreciate the clarity and consistency.
Training compliance requires more than theoretical knowledge. Practical application and documented proof distinguish companies that breeze through inspections from those that stumble. GxP Training’s Regulatory Compliance Inspections and External Audits course delivers a focused, interactive experience designed by Regulatory Affairs experts with Northeastern University qualifications and validated by senior auditors.

Course features include:
Downloadable certificates and completion data integrate directly into your master training log. Auditors gain instant access to traceable proof that your team mastered every required topic.
Complete records form the backbone of audit proof. Start with an up-to-date export of your master training log from your learning management system. Next, assemble each employee’s certificates of completion alongside signed attendance sheets or digital confirmation receipts. Include exam score reports or quiz results that demonstrate understanding of key concepts.
Informal sessions such as on-the-job demonstrations or toolbox talks require documentation too. Create a simple acknowledgement form where participants and trainers sign off on topics covered. Store these forms in individual folders, dated and signed.
Course syllabi, slide decks and SOP snippets belong in your course materials archive. Verify that every document displays an effective date and version matching the training date in your log. Cross-reference your materials archive with the revision log to show how content evolved and that retraining occurred promptly.
Traceability extends beyond filing. Auditors expect clear evidence of approval at every step. Attach trainer and supervisor signatures or electronic verifications to each certificate or attendance record. Electronic systems must capture user identity, timestamp and change logs in compliance with FDA 21 CFR Part 11.
Role-based competency maps strengthen your proof of compliance. Link each training module back to specific job descriptions and responsibilities. Insert a competency matrix in your file that shows which courses align with which roles. This map illustrates that your training program reflects the actual needs of your workforce and meets regulatory expectations.
Internal audits reveal gaps before external inspectors arrive. Develop a checklist derived from ICH Q10, FDA and WHO guidelines that covers completeness, currency and audit-trail requirements. Review your file section by section, marking missing dates, unsigned forms or mismatched versions.
Where gaps appear, document them in a corrective action log. Schedule make-up training sessions or update records immediately. Record these actions with dates, responsible parties and completion evidence. Auditors respect organisations that identify issues proactively and follow through with corrective measures.
Presentation enhances audit efficiency. In physical binders, add colour-coded tabs and a quick-start section containing a matrix snapshot, sample certificates and a SOP version list. Digital folders benefit from a hyperlinked contents page that leads reviewers to key documents at the click of a link.
Training compliance remains a dynamic process. New hires require induction training within their first month, and completion should be recorded without delay. SOP revisions, regulatory updates or business changes warrant targeted refresher courses. Trigger retraining automatically when your revision log captures an update to procedures or guidelines.
Retention requirements vary by jurisdiction but typically mandate retaining records for at least two years following product discontinuation or per local laws. Store electronic records in a secure, access-controlled repository with routine backups. Maintain any required paper copies in a controlled environment to support rapid retrieval.
Regulatory audits test the strength of your training program and the clarity of your documentation. Life-science quality teams that present a complete, well-structured set of records streamline inspections and minimise findings. GxP Training’s Regulatory Compliance Inspections and External Audits course delivers the detailed guidance, case studies and accredited certificates required to demonstrate your commitment to quality. Equip your team with this focused training program and transform your records into incontrovertible proof of compliance.
